Secret program with around 300.000 victims
Aktion T4: Nazi Euthanasia Program

Aktion T4, the Nazi program for involuntary euthanasia
Aktion T4 (The name T4 is derived from the address of their office, Tiergartenstraße 4 in Berlin) was the name for the mass murder by involuntary euthanasia in Nazi Germany's eugenics program based on "mercy killing" and mandatory sterilization. As soon as 1925, in his book "Mein Kampf", Hitler left no doubt that in the long run, only the Aryan race had the right to exist. When the National Socialists came to power in 1933, the improvement of the race of the German people was therefore high on the agenda. For example, with the introduction of the Nuremberg Race Laws, sexual relations and marriages between Aryans and non-Aryans were banned. Almost at the same time, the “Lebensborn project” was launched, which aims to increase the birth rate of pure bred Aryan children.
Who was responsible for Aktion T4?
The program started in October 1939 on the orders of Adolf Hitler. The office that had to implement this Sonderprogram worked under the leadership of Philipp Bouhler a German senior Nazi Party functionary who was both a Reichsleiter (National Leader) and Chief of the Chancellery of the Führer of the NSDAP. He was also the SS official responsible for the Aktion T4 euthanasia program that killed more than 250.000 disabled adults and children in Nazi Germany. Bouhler was also the co-initiator of Aktion 14f13, also called "Sonderbehandlung" ("special treatment") that killed between 15.000 - 20.000 concentration camp prisoners. The combination of numbers and letters 14f13, was derived from the SS's meticulous system of record keeping. The number "14" referred to the Concentration Camps Inspector, the letter "f" stood for "deaths" (in German "Todesfälle"), and the number "13" indicated the method of execution, specifically gassing at the T4 killing centers. The term "Sonderbehandlung" (special treatment) was a euphemism used to denote execution or killing. In 1941, Bouhler and Heinrich Himmler launched Aktion 14f13. Bouhler directed Viktor Brack, head of Hitler's Chancellery Hauptamt II, to execute this directive. Brack, who already oversaw T4's diverse front operations, was entrusted with its implementation.
Also appointed as an organiser was Karl Brandt Hitler's personal physician. Trained in surgery, Brandt joined the Nazi Party in 1932. A member of Hitler's inner circle at the Berghof, he was selected by Philipp Bouhler, the head of Hitler's Chancellery, to administer the Aktion T4 euthanasia program. Brandt was later appointed the Reich Commissioner of Sanitation and Health (Bevollmächtigter für das Sanitäts- und Gesundheitswesen). Accused of involvement in human experimentation and other war crimes, Brandt was indicted in late 1946 and faced trial before a US military tribunal along with 22 others in United States of America v. Karl Brandt. He was convicted, sentenced to death and later hanged on 2 June 1948.
Hauptamt II officials, led by Viktor Brack, were crucial in orchestrating the Aktion T4 'euthanasia' program, which targeted mentally ill and physically handicapped individuals. Beginning in 1939, they played a significant role in the child 'euthanasia' efforts. The actual execution of these killing operations was managed by subordinates like Brack. On August 20, 1947, Brack received a death sentence. Viktor Brack was tried and executed by hanging at Landsberg Prison on June 2, 1948. As he stood at the gallows, he expressed a final wish for God to bring peace to the world.

Individuals responsible for initiating the Aktion T4 program
Philipp Bouhler
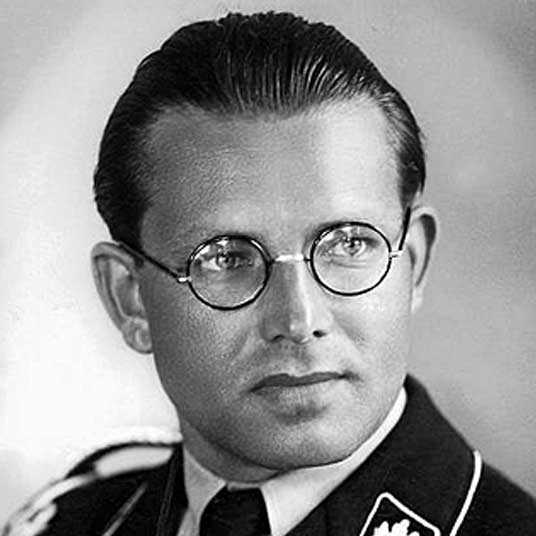

Died: 19 May 1945 (aged 45)
Karl Brandt
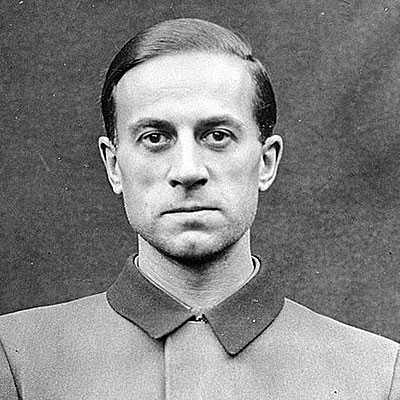

Died: 19 May 1945 (aged 44)
Viktor Hermann Brack
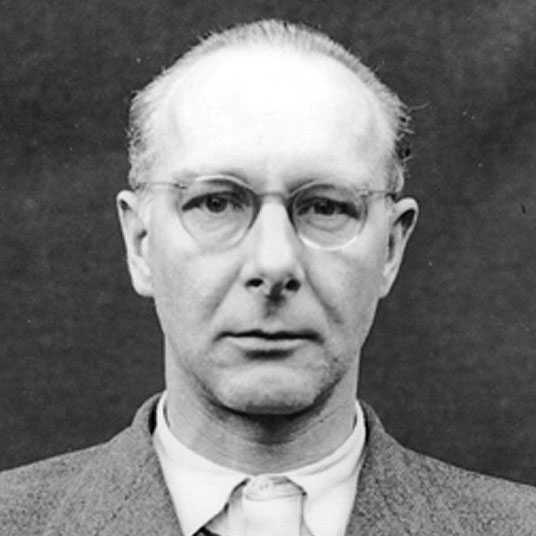

Died: 2 June 1948 (aged 43)
What objective did Aktion T4 aim to achieve?
The goal of the Aktion T4 program was to preserve the genetic purity of the Germanic people by systematically murdering people who were disfigured, disabled or suffering from some form of psychiatric illness. Arguments to justify this murder were the in Nazi eyes "meaningless existence" and the "meaningless suffering" of these patients.
Aktion T4 was designed to facilitate of purification program was called "mercy killing" because the Nazi doctors saw it as an act of mercy and presented it as the most humane way to put these sick out of their suffering. This thesis belonged to Karl Brandt, Gruppenführer in the SS and Generalleutnant in the Waffen-SS and one of the people who initiated the Aktion T4. He was sentenced to death in the Medical Trial, one of the Nuremberg Trials, and later hanged. In addition, there were also economic considerations: those who worked in the care of the disabled could not serve as a soldier or work in the war industry.
Disabled children were separated from their families and taken to special hospitals. The media at the time responded to the fear that within a few years a large part of the German people would be mentally disturbed, reason to act as quickly as possible. The word "euthanasia" was not used in Nazi propaganda about the Aktion T4, leaving the real intentions of the Nazis (at the beginning) undiscovered. The program was later expanded to include adults, most of whom underwent compulsory sterilization.
How were the patients brought to the euthanasia centers?
Nurses and doctors played a disturbing role in the euthanasia process, deceiving patients about their destination and purpose of transport. These healthcare professionals, who were ostensibly there to care for the sick, instead facilitated their demise.
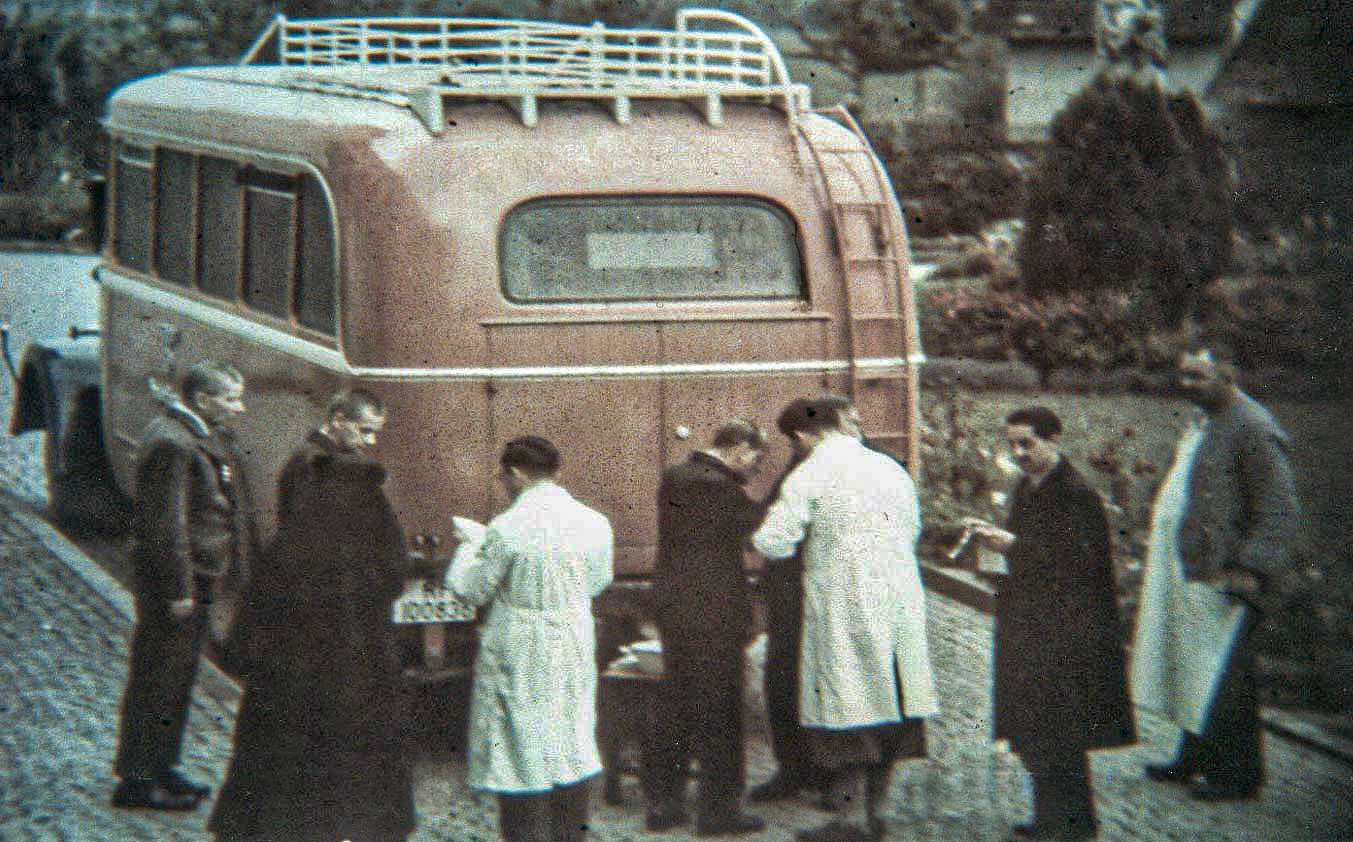


When the innocent victims arrived at the designated euthanasia centers, they were initially directed to a reception area. A doctor would then assess their condition to determine eligibility for euthanasia. If deemed eligible, they were tragically led to a gas chamber and killed.
The Nazi regime meticulously concealed the Aktion T4 program from public scrutiny. Fearing public outcry and exposure of their horrific actions, they employed deceptive tactics to transport patients to euthanasia centers under the guise of medical treatment.

Involuntary euthanasia on disabled patients
The involuntary euthanaisa of the Aktion T4, was carried out by gassing, asphyxiation, injections, poisoning, starvation and drug overdoses. The first experiments with gas vans were carried out in March 1940 at the hospital in Kochanowka near Łódź. Soon after, the Nazis conducted further experiments in which they poured carbon monoxide from the exhaust of a truck into a closed room. Many of these exterminations during the Aktion T4, were overseen by psychiatrists Carl Hans Heinze Sennhenn and Werner Villinger. Sennhenn supplied hundreds of brains to Nazi researchers. Werner Villinger conducted experiments on humans before sending them to death. Even before the Holocaust and to carry out the Aktion T4, the first gas chambers were built in Hartheim, where adults in particular were killed with carbon monoxide.
Medical personnel paid to kill
The SS functionaries and hospital staff associated with Aktion T4 in the German Reich were paid from the central office at Tiergartenstraße 4 in Berlin from the spring of 1940. The SS and police from SS-Sonderkommando Lange responsible for murdering the majority of patients in the annexed territories of Poland since October 1939, took their salaries from the normal police fund, supervised by the administration of the newly formed Wartheland district; the programme in Germany and occupied Poland was overseen by Heinrich Himmler.

How many disabled and psychiatric patients died because of Aktion T4?
Before 2013 it was believed, that during the Aktion T4, approximately 70.000 people were murdered in the euthanasia programme. Recently the German Federal Archives reported that research in the archives of former East Germany indicated that the number of victims in Germany and Austria from 1939 to 1945 was about 200.000 people and that another 100.000 people were victims in other European countries.
The German Aktion T4 centers upheld the resemblance of legality in keeping records and writing letters. In Polish psychiatric hospitals no one was left behind during the Aktion T4. Killings were inflicted using gas-vans, sealed army bunkers and machine guns; families were not informed about the murdered relatives and the empty wards were handed over to the SS.
The Aktion T4 Euthanasia Center locations
Unveiling the victims of the Aktion T4 Program
Aktion T4 stands as a harrowing crime against humanity, where victims were unjustly murdered solely for their differences. This dark chapter in German history serves as a poignant reminder of the perils of intolerance and discrimination.
Honoring the memory of those affected by Aktion T4 is crucial, not only to commemorate their lives but also to advocate against any form of dehumanization or prejudice. By preserving their memory, we strive towards a future that values empathy and inclusivity, safeguarding and cherishing the inherent dignity of every human life.
Temporary stop due to pressure from the church
On 18 August 1941, Hitler temporarily halted the program under pressure from Cardinal Clemens August von Galen of the Catholic Church, other churches and families of the victims. More than 70.000 people had already been murdered by then. The German public resistance slowed down but not completely halted; the program was continued in utmost secrecy. Trained troops kept going. Some parts of the program were transferred to military concentration camps.
The murder of the disabled patients continues
But the program did not stop in 1941. Doctors and nurses continued to perform in hospitals in Germany, Austria and Poland. The murders were carried out in such a way that the mistrust of the German population was minimized.
Such precautions however were not taken when people from the occupied territories were murdered. Brutal and violent action have been reported and recorded. The total of victims of the Aktion T4 program in the Nazi occupied territories is estimated at around 100.000 people.
Many of those involved in the program also took an active part in the Holocaust. Some of them were engaged in the development of the gas chambers in Bełżec, Treblinka and Sobibór extermination camps as part of Aktion Reinhard. Besides Auschwitz-Birkenau, Majdanek and Chełmno, these were the main sites of the murder of millions of people.
The results of the Aktion T4 program
Aktion T4, the Nazi Euthanasia program in Germany, killed an estimated 200.000 people. By the end of 1941, every third resident of a mental institution in Germany was already dead, either from murder or from starvation, resulting in 93.000 available beds.
Hitler's grandniece, Aloisia Veit, was among the victims
Aloisia Veit, the niece of Adolf Hitler, was killed in the Nazi euthanasia program in December 1940. She was 49 years old and had schizophrenia. Veit's inclusion in the program was likely due to rumors that circulated among the Nazi leadership about a mental illness in Hitler's family. It is not clear whether Hitler himself knew that his niece had been killed. However he was aware of the euthanasia program and approved of it.
What happened with the perpetrators after the war?
Many of the doctors and nurses who participated in the program were never brought to justice. Some were tried and convicted after the war, but others escaped prosecution. In 1961, a West German court convicted 16 people for their role in the Nazi euthanasia program. However, many other perpetrators were never brought to justice.A monument to the victims of the Nazi euthanasia program was finally laid in Tiergartenstraße, Berlin, on 8 July 2013. The monument is dedicated to the memory of the 200,000 to 300,000 people who were killed in the program. The monument is a reminder of the horrors of the Nazi euthanasia program and the importance of fighting against all forms of discrimination and intolerance.
Clemens A. von Galen
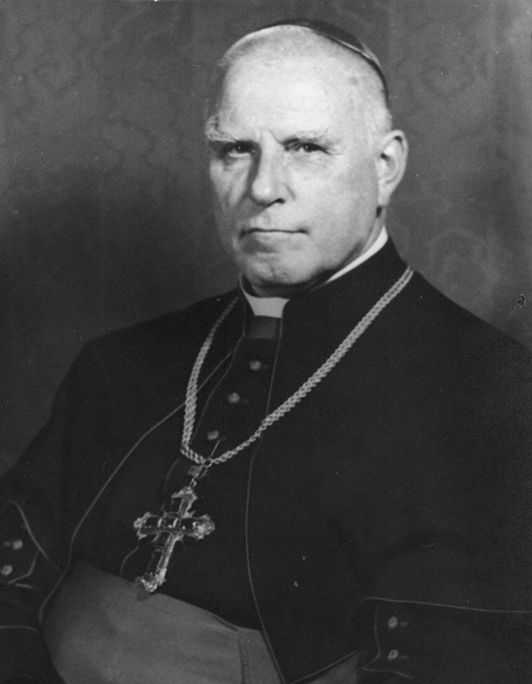

Born: Dinklage, 16 march 1878
Died: Münster, 22 march 1946
Aloisia Veit

The stories on my website are meant to educate people about WW2. You can help by sharing them with your family and friends on your social platforms. Thank you so much for your assistance.